Mastering Device Driver Management in Windows 7: A Comprehensive Guide
In the intricate ecosystem of computer hardware and software, device drivers play a crucial role in facilitating communication between hardware components and the operating system. Windows 7, one of Microsoft’s most popular operating systems, provides robust tools and utilities for managing device drivers, ensuring compatibility, stability, and optimal performance of hardware devices. From updating drivers to troubleshooting driver-related issues, understanding how to manage device drivers effectively is essential for maintaining a smoothly functioning system. In this exhaustive guide, we will delve deep into the intricacies of managing device drivers in Windows 7, providing step-by-step instructions, advanced techniques, and practical insights to help you navigate the complexities of driver management with confidence.
Understanding Device Drivers in Windows 7:
Before diving into the process of managing device drivers, let’s first grasp the concept and significance of device drivers in Windows 7:
- Definition: Device drivers are software components that enable the operating system to communicate with hardware devices, such as printers, graphics cards, network adapters, and storage devices.
- Functionality: Device drivers facilitate the exchange of data and commands between the operating system and hardware devices, allowing users to interact with and utilize hardware resources effectively.
- Compatibility and Stability: Ensuring that device drivers are up-to-date and compatible with the operating system is essential for maintaining system stability, preventing hardware conflicts, and optimizing performance in Windows 7.
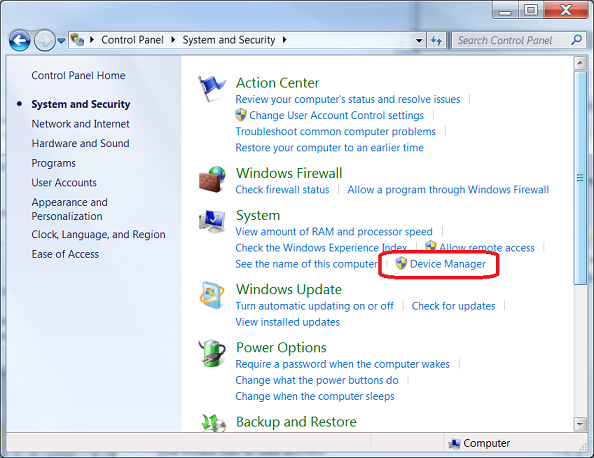
Accessing Device Manager in Windows 7:
Now, let’s explore how to access and navigate Device Manager, the primary tool for managing device drivers in Windows 7:
- Accessing Device Manager:
- Click on the Start button in the taskbar.
- Right-click on “Computer” or “This PC” and select “Manage” from the context menu to open the Computer Management window.
- In the Computer Management window, navigate to “Device Manager” under the System Tools section.
- Navigating Device Manager:
- Device Manager provides a hierarchical view of hardware devices categorized into different types, such as Display adapters, Network adapters, Sound, video, and game controllers, etc.
- Expand each category to view the list of devices and their corresponding drivers.
Managing Device Drivers in Windows 7:
Now that we’ve accessed Device Manager, let’s explore how to manage device drivers effectively:
- Updating Device Drivers:
- Right-click on the device you want to update in Device Manager and select “Update Driver Software” from the context menu.
- Choose between searching automatically for updated driver software or browsing your computer for driver software, depending on your preference.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the driver update process.
- Rolling Back Device Drivers:
- If a newly installed driver causes issues or compatibility problems, you can roll back to the previous driver version.
- Right-click on the device with the problematic driver in Device Manager and select “Properties.”
- Navigate to the “Driver” tab and click on the “Roll Back Driver” button if available. Follow the on-screen instructions to roll back the driver.
- Disabling and Enabling Device Drivers:
- Right-click on the device you want to disable or enable in Device Manager and select “Disable” or “Enable” from the context menu.
- Disabling a device driver prevents it from functioning until it is enabled again, which can be useful for troubleshooting purposes or temporarily deactivating hardware devices.
- Uninstalling Device Drivers:
- Right-click on the device whose driver you want to uninstall in Device Manager and select “Uninstall” from the context menu.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to uninstall the device driver. You may be prompted to restart your computer after the uninstallation process is complete.
Advanced Features and Tips:
To further optimize your experience with device driver management in Windows 7, consider the following advanced features and tips:
- Viewing Hidden Devices:
- Enable the display of hidden devices in Device Manager to view devices that are not currently connected to your computer or are hidden for other reasons.
- Click on the “View” menu in Device Manager and select “Show hidden devices” to reveal hidden devices.
- Exporting and Importing Device Drivers:
- Use third-party utilities or built-in tools to export and import device drivers for backup or migration purposes.
- Explore options for exporting and importing device drivers to ensure seamless driver management across multiple systems.
- Using Compatibility Mode:
- If you encounter compatibility issues with certain device drivers, consider using compatibility mode to run drivers designed for previous versions of Windows.
- Right-click on the driver installation file, select “Properties,” navigate to the “Compatibility” tab, and enable compatibility mode for the desired Windows version.
- Seeking Manufacturer Support:
- If you encounter persistent issues with device drivers, consider seeking support from the manufacturer’s website or customer support channels.
- Manufacturers often provide updated drivers, troubleshooting guides, and support forums to help users resolve driver-related issues.
Conclusion:
Managing device drivers is a critical aspect of maintaining a stable and efficient computing environment in Windows 7. By following the comprehensive guide outlined above, users can effectively update, roll back, disable, enable, and uninstall device drivers using Device Manager. Whether it’s optimizing hardware compatibility, resolving compatibility issues, or troubleshooting driver-related problems, understanding how to manage device drivers is essential for ensuring the smooth operation of hardware devices in Windows 7. So take control of your device drivers today, master device driver management with confidence, and unlock new possibilities for compatibility, stability, and performance in Windows 7.







