Mastering SolidWorks: A Comprehensive Guide to Sketching Lines
Introduction: SolidWorks is a leading computer-aided design (CAD) software that empowers engineers, designers, and manufacturers to create precise 3D models of mechanical parts, assemblies, and products. At the core of SolidWorks lies sketching, the process of creating 2D profiles that serve as the foundation for 3D geometry. Among the basic sketching tools available, the line tool holds a prominent place for creating straight segments and defining the boundaries of geometric shapes. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore step-by-step instructions, tips, and best practices for sketching lines in SolidWorks, enabling users to master this essential skill and efficiently create linear features in their designs.
Understanding the Importance of Sketching Lines: Lines are fundamental elements of geometry that form the basis for creating complex shapes, profiles, and structures in SolidWorks. Sketching lines allows users to define the boundaries, edges, and contours of geometric features, providing the framework for creating intricate designs with precision and accuracy. Whether you’re designing mechanical parts, architectural layouts, or industrial components, the ability to sketch lines accurately and efficiently is essential for achieving design intent and maintaining geometric integrity throughout the modeling process.
Key Components of Sketching Lines: Before we delve into the process of sketching lines in SolidWorks, let’s familiarize ourselves with the key components involved:
- Sketch Plane: A sketch plane is a 2D surface within the SolidWorks environment where sketches are created. Common sketch planes include the Front Plane, Top Plane, Right Plane, and custom reference planes.
- Line Tool: The Line tool in SolidWorks allows users to create straight segments by specifying the start and end points of each segment.
- Sketch Relations: Sketch relations are geometric constraints applied to sketch entities to maintain their relationships and ensure dimensional accuracy. Common sketch relations for lines include horizontal, vertical, parallel, perpendicular, and equal.
- Dimensions: Dimensions are numerical values applied to sketch entities to define their size, position, and relationships relative to other geometry. Dimensions can be added manually or inferred automatically based on geometric constraints.
Sketching a Line in SolidWorks: Now, let’s walk through the step-by-step process of sketching a line in SolidWorks:
Step 1: Open a New Sketch
- Launch SolidWorks software and open a new or existing part document.
- Select the desired sketch plane where you want to sketch the line. Common options include the Front Plane, Top Plane, or custom reference planes.
Step 2: Activate the Line Tool
- Once the sketch plane is selected, activate the Line tool from the Sketch tab on the Command Manager or the Sketch toolbar.
- Alternatively, press the keyboard shortcut “L” to access the Line tool directly.
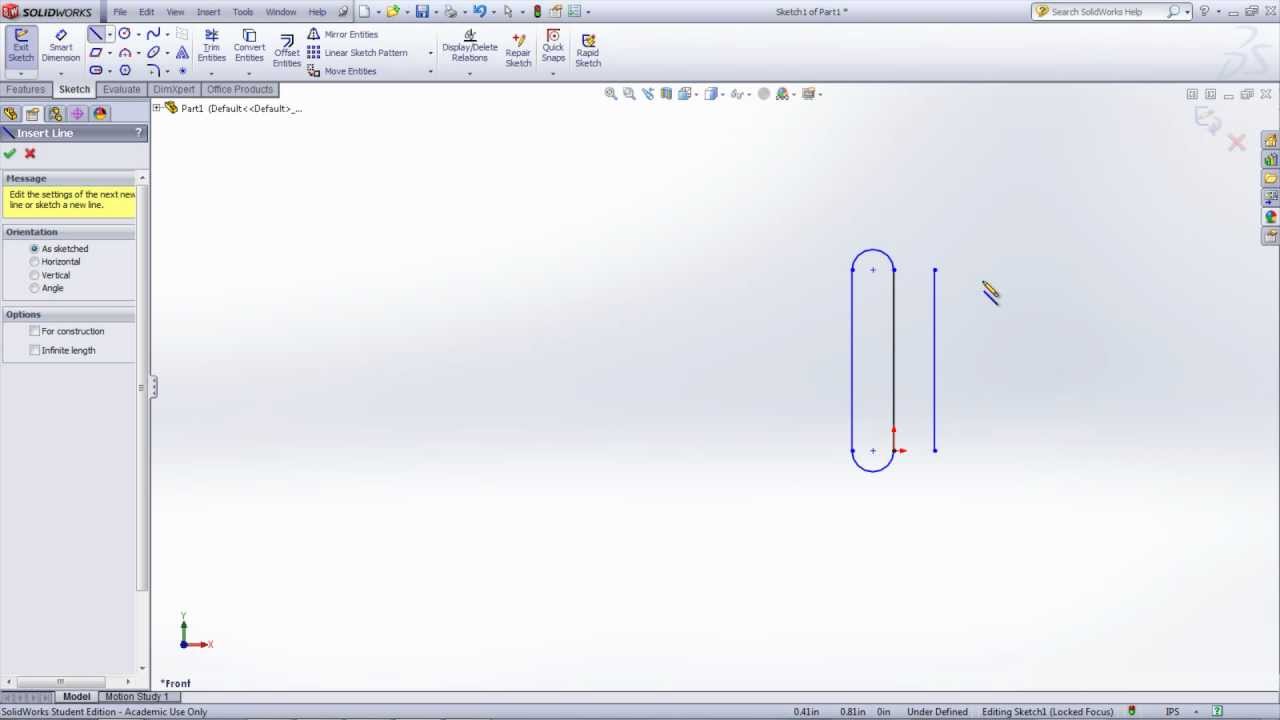
Step 3: Define the Line
- Click on the sketch plane to specify the start point of the line segment.
- Move the cursor to define the end point of the line segment, then click again to complete the line.
- Repeat the process to create additional line segments as needed to define the desired shape or profile.
Step 4: Apply Dimensions (Optional)
- After creating the line segments, apply dimensions to define their lengths, angles, and positions. Click on the line segments to add dimensions using the Smart Dimension tool.
- Enter numerical values for the dimensions to specify the desired lengths and angles accurately.
Step 5: Add Sketch Relations (Optional)
- Apply sketch relations to maintain geometric constraints and relationships between the line segments. Use constraints such as horizontal, vertical, parallel, perpendicular, and equal to ensure dimensional accuracy and consistency.
Step 6: Exit the Sketch
- Once the lines are fully defined, exit the sketch environment by clicking on the “Exit Sketch” button or by pressing the keyboard shortcut “Ctrl + Q.”
Step 7: Review and Validate
- Review the sketch to ensure that the lines are accurately defined and meet the design requirements.
- Verify the dimensions, relations, and geometric properties of the lines using SolidWorks tools such as Measure, Evaluate, and SketchXpert.
Step 8: Save the Part
- Save the part document to a location on your computer or network using a descriptive filename that reflects the content or purpose of the part.
- Choose the appropriate file format (e.g., SolidWorks Part (*.sldprt)) and version compatibility options as needed.
Advanced Techniques for Sketching Lines: In addition to the basic steps outlined above, SolidWorks offers several advanced techniques and features for sketching lines with precision and efficiency. Here are some advanced techniques you can explore:
- Construction Lines: Use construction lines to create reference geometry that assists in sketching and dimensioning. Construction lines are temporary and do not contribute to the final geometry of the sketch.
- Centerlines: Centerlines are special types of construction lines used to define the center axis or symmetry axis of cylindrical or rotational features. Centerlines aid in sketching symmetric profiles and features.
- Offset Entities: The Offset Entities tool allows you to create parallel or concentric copies of existing sketch entities, including lines. This tool is useful for creating offsets, clearances, and boundaries within sketches.
Best Practices for Sketching Lines: To sketch lines efficiently and accurately in SolidWorks, consider the following best practices:
- Plan Ahead: Before sketching lines, visualize the desired shape, profile, and layout within the design context. Consider factors such as functionality, aesthetics, and manufacturability to guide your decisions.
- Use Sketch Relations: Apply sketch relations to maintain geometric constraints and relationships between the line segments. Use constraints such as horizontal, vertical, parallel, perpendicular, and equal to ensure dimensional accuracy and consistency.
- Apply Dimensions Strategically: Use dimensions strategically to define the critical lengths, angles, and positions of the lines. Focus on dimensions that are essential for the design intent and functionality, and avoid over-dimensioning or redundant dimensions.
- Leverage Parametric Modeling: Take advantage of parametric modeling techniques to create lines with dimensions and parameters that are driven by mathematical equations or design parameters. Parametric modeling allows for flexible and adaptive designs that can be easily modified and updated.
Conclusion: Sketching lines is a fundamental skill in SolidWorks that enables users to create precise profiles, shapes, and boundaries with ease and precision. By following the step-by-step instructions, tips, and best practices outlined in this guide, you can master the art of sketching lines and efficiently create linear features for your designs. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, mastering the fundamentals of sketching lines empowers you to unleash your creativity and design innovative components and assemblies in SolidWorks. So next time you embark on a new design project, remember the principles and techniques shared in this guide to sketch lines with confidence and proficiency.