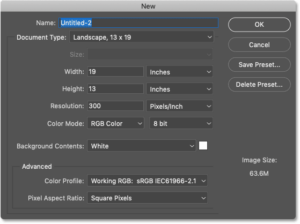
Preserving Perfection: A Comprehensive Guide on How to Avoid Losing Your Original Images in Photoshop
Introduction: Adobe Photoshop, a digital playground for creativity, allows users to manipulate and enhance images with unparalleled precision. Amidst the...