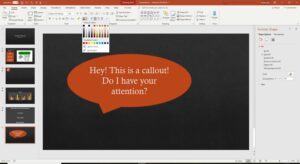
Enhancing Visual Communication: A Comprehensive Guide to Adding Callouts to Images in PowerPoint 2010
Introduction: In today's digital age, effective visual communication is essential for capturing audience attention, conveying messages clearly, and engaging viewers....