Mastering Windows Task Scheduler: A Comprehensive Guide to Harnessing the Power of Task Automation in Windows 7
In the fast-paced world of computing, efficiency and productivity are paramount. Windows Task Scheduler, a powerful built-in utility of Windows 7, empowers users to automate repetitive tasks, schedule maintenance activities, and streamline workflow processes with ease. From running backup scripts to launching applications at specific times, Task Scheduler offers a wide range of functionalities to enhance productivity and convenience. In this exhaustive guide, we will delve deep into the intricacies of Windows Task Scheduler, providing step-by-step instructions, advanced techniques, and practical examples to help you leverage its capabilities effectively.
Understanding Windows Task Scheduler in Windows 7:
Before diving into the process of using Windows Task Scheduler, let’s first grasp the concept and significance of this indispensable tool:
- Definition: Windows Task Scheduler is a system utility in Windows 7 that enables users to automate the execution of tasks, programs, and scripts at predefined intervals or in response to specific events.
- Task Automation: Task Scheduler allows users to automate a wide range of tasks, including system maintenance, software updates, file backups, and application launches, eliminating the need for manual intervention and saving time and effort.
- Flexibility and Customization: Task Scheduler offers a high degree of flexibility and customization, allowing users to define task triggers, set execution conditions, and specify task actions based on their specific requirements and preferences.
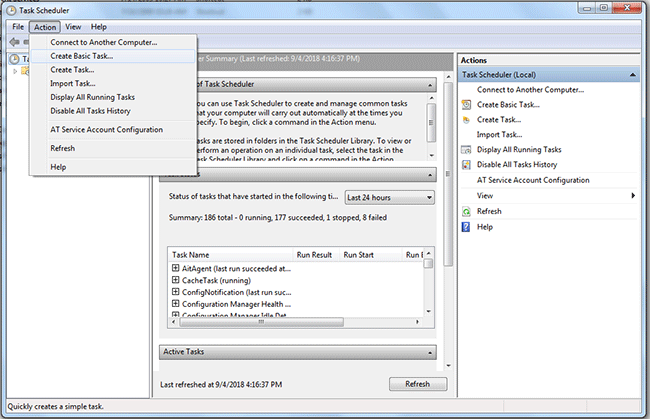
Accessing Windows Task Scheduler:
Now, let’s explore how to access and navigate Windows Task Scheduler in Windows 7:
- Accessing Task Scheduler:
- Click on the Start button in the taskbar.
- Open the Control Panel and navigate to the “System and Security” category.
- Click on “Administrative Tools” and then double-click on “Task Scheduler” to launch the Task Scheduler application.
- Navigating Task Scheduler:
- The Task Scheduler window provides a hierarchical view of tasks organized into folders and categories.
- Navigate through the folders to view existing tasks, create new tasks, or modify task properties.
Using Windows Task Scheduler:
Now that we’ve accessed Task Scheduler let’s explore how to use its features and functionalities effectively:
- Creating a Basic Task:
- Click on “Create Basic Task” in the Actions pane to launch the Create Basic Task Wizard.
- Follow the wizard prompts to specify a name and description for the task, set the trigger (e.g., daily, weekly, monthly), and define the action (e.g., start a program, send an email).
- Creating a Custom Task:
- Click on “Create Task” in the Actions pane to open the Create Task dialog.
- Configure task settings such as triggers, conditions, actions, and settings in the various tabs of the Create Task dialog to create a custom task tailored to your specific requirements.
- Modifying Existing Tasks:
- Double-click on an existing task in the Task Scheduler window to open its properties.
- Modify task properties such as triggers, actions, conditions, and settings as needed to update or customize the task.
- Viewing Task History and Status:
- Use the “History” tab in the Task Scheduler window to view the execution history and status of tasks.
- Monitor task execution, view completed, failed, or missed tasks, and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
Advanced Features and Tips:
To further enhance your experience with Windows Task Scheduler, consider the following advanced features and tips:
- Using Task Actions and Conditions:
- Explore advanced task actions and conditions to create more sophisticated task workflows.
- Use actions such as running PowerShell scripts, sending emails, or displaying messages to perform complex task operations.
- Managing Task Triggers:
- Customize task triggers to launch tasks based on specific events, system startup or shutdown, user logon or logoff, or idle time.
- Fine-tune trigger settings to optimize task execution and responsiveness.
- Utilizing Task Libraries and Templates:
- Explore the built-in task libraries and templates provided by Windows Task Scheduler for common tasks and operations.
- Use task templates as starting points for creating new tasks or managing existing tasks more efficiently.
- Monitoring Task Performance:
- Use performance monitoring tools and utilities to track the resource usage and performance impact of scheduled tasks.
- Monitor CPU, memory, disk, and network usage to ensure that scheduled tasks do not adversely affect system performance.
Conclusion:
Windows Task Scheduler is a powerful tool that empowers users to automate tasks, streamline workflow processes, and enhance productivity in Windows 7. By following the comprehensive guide outlined above, users can harness the capabilities of Task Scheduler to schedule routine tasks, automate maintenance activities, and optimize system performance with ease. Whether it’s running backup scripts, launching applications, or performing system maintenance, Task Scheduler provides users with the tools and flexibility to automate tasks efficiently and effectively. So embrace the power of task automation today, leverage Windows Task Scheduler with confidence, and unlock new possibilities for productivity and convenience in Windows 7.







