Mastering Toolpath Templates: A Comprehensive Guide to Creating Custom CNC Machining Strategies
Introduction: Creating toolpath templates is an essential skill for CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machinists and programmers seeking to streamline their workflow, increase productivity, and maintain consistency across multiple machining projects. Toolpath templates allow users to define and save customized machining strategies for common operations, such as roughing, finishing, and drilling, which can then be easily applied to new parts and components. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of creating toolpath templates, covering everything from software options to best practices and advanced techniques. Whether you’re a novice CNC machinist or an experienced professional looking to optimize your processes, this guide will provide you with the essential knowledge and skills you need to master the art of creating toolpath templates.
Understanding Toolpath Templates: Before diving into the specifics of creating toolpath templates, it’s important to understand what they are and how they function within the CNC machining process. Toolpath templates are essentially pre-defined sets of cutting instructions that dictate how the CNC machine will move its cutting tool (such as a mill or router) to shape and carve a workpiece according to a specific design. By creating templates for common machining operations, users can save time and effort by avoiding the need to manually program toolpaths for each new project.
Choosing the Right Software: The first step in creating toolpath templates is selecting the right software for the job. There are a variety of CAD/CAM software options available on the market, each with its own set of features and capabilities for creating and managing toolpaths. Some popular options include Autodesk Fusion 360, SolidWorks CAM, RhinoCAM, and Mastercam, among others. When choosing software, it’s important to consider factors such as compatibility with your CNC machine, ease of use, and the specific features you need for your projects.
Identifying Common Machining Operations: Once you’ve selected your CAD/CAM software, the next step is to identify the common machining operations that you want to create templates for. This may include operations such as roughing, finishing, drilling, pocketing, and contouring, among others. By identifying the most common operations in your workflow, you can prioritize which templates to create first and focus your efforts on those that will provide the greatest benefit.
Creating Custom Toolpath Strategies: With your common machining operations identified, the next step is to create custom toolpath strategies for each one. This may involve selecting the appropriate cutting tools, specifying cutting parameters such as speeds and feeds, defining toolpath patterns and depths of cut, and optimizing toolpath order for maximum efficiency and accuracy. Depending on your software and machining requirements, you may also have the option to create advanced toolpath strategies such as adaptive clearing, high-speed machining, and 5-axis milling.
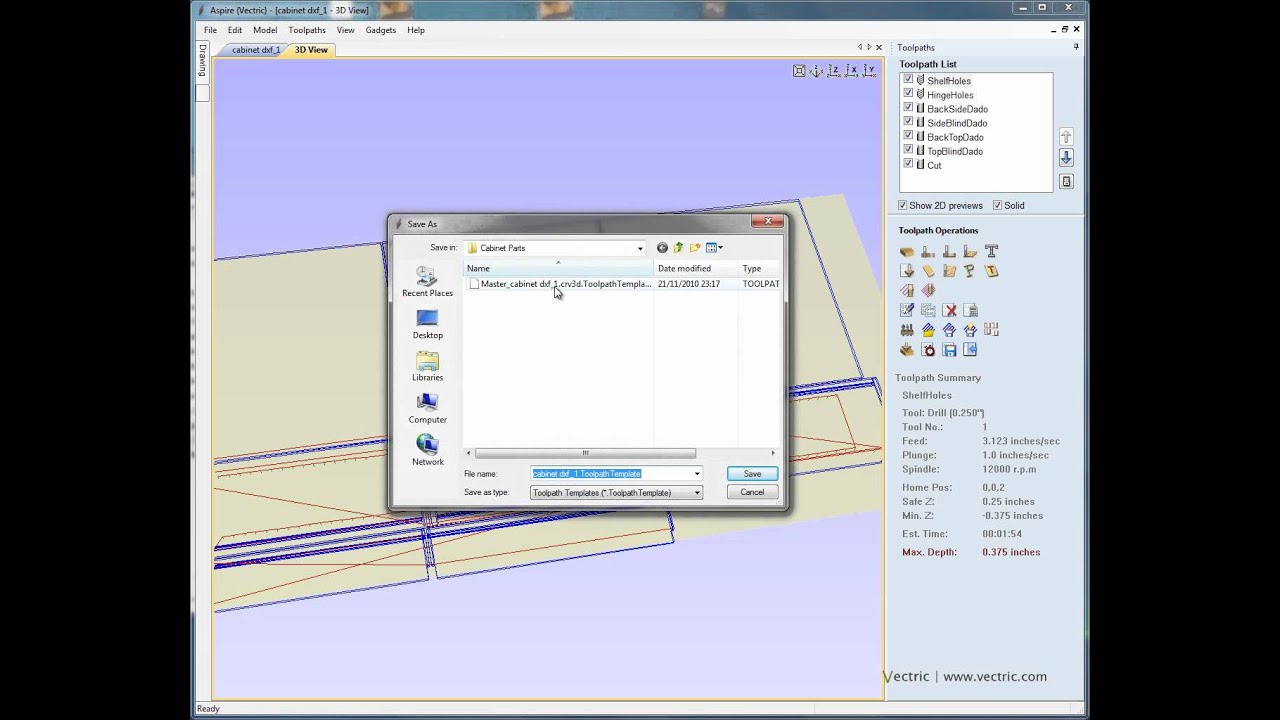
Organizing and Managing Templates: Once you’ve created your toolpath templates, it’s important to organize and manage them effectively for easy access and retrieval. Most CAD/CAM software packages offer tools for organizing and managing toolpath templates, such as libraries or folders where templates can be stored and categorized based on their type, material, or machining operation. By keeping your templates organized and well-documented, you can ensure that they are readily available when needed and that they remain consistent and up-to-date across multiple projects.
Applying Templates to New Projects: With your toolpath templates created and organized, the final step is to apply them to new projects as needed. This may involve importing your CAD model into your CAM software, selecting the appropriate template for each machining operation, and then adjusting any parameters or settings as necessary to customize the toolpaths for the specific requirements of the project. By leveraging your toolpath templates effectively, you can streamline your workflow, reduce programming time, and achieve consistent and reliable machining results across all of your projects.
Best Practices and Advanced Techniques: To get the most out of your toolpath templates, it’s important to follow best practices and explore advanced techniques for customization and optimization. Some tips for creating and using toolpath templates include:
- Standardizing tooling and cutting parameters across all templates to ensure consistency and repeatability.
- Regularly reviewing and updating templates to incorporate new tools, technologies, and best practices.
- Experimenting with different toolpath strategies and parameters to optimize machining efficiency and surface finish quality.
- Leveraging features such as parametric templates or macro programming to create dynamic and adaptive toolpath templates that can adjust to changing machining requirements.
Conclusion: Creating toolpath templates is an essential skill for CNC machinists and programmers seeking to optimize their workflow, increase productivity, and maintain consistency across multiple projects. By understanding the fundamentals of toolpath creation, choosing the right software, identifying common machining operations, and following best practices for organization and management, you can create customized templates that streamline your workflow and produce reliable and consistent machining results. With the knowledge and techniques outlined in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to master the art of creating toolpath templates and unlock the full potential of CNC machining in your manufacturing operations.







