Mastering AutoCAD’s 3D Orbit and View Commands: Enhancing Your 3D Modeling Experience
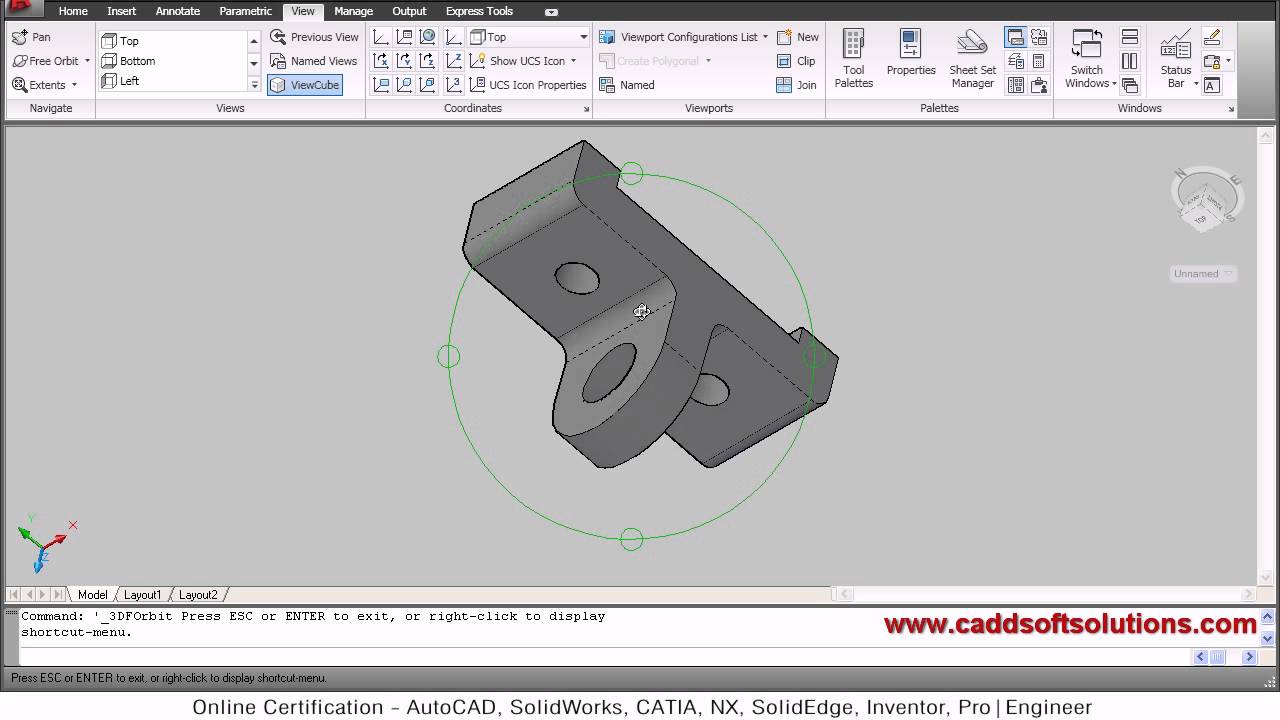
AutoCAD’s 3D Orbit and View commands are indispensable tools for navigating and manipulating 3D models with ease and precision. Whether you’re a seasoned CAD professional or just starting out with 3D modeling, mastering these commands can greatly enhance your workflow and productivity. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about AutoCAD’s 3D Orbit and View commands, from basic navigation techniques to advanced tips and tricks for achieving optimal results.
1. Understanding 3D Orbit:
The 3D Orbit command in AutoCAD allows users to freely rotate and manipulate the view of a 3D model in all three dimensions. To activate the 3D Orbit command, simply type “3DORBIT” into the command line and press Enter, or click on the Orbit icon in the ViewCube navigation bar. Once activated, you can use the mouse to orbit the view around the model, zoom in and out, and pan the view to focus on specific areas.
2. Basic Navigation Techniques:
When using the 3D Orbit command, there are several basic navigation techniques that can help you navigate and manipulate your 3D model more effectively. These include:
- Left-click and drag to orbit the view around the model.
- Scroll the mouse wheel to zoom in and out.
- Hold down the Shift key while dragging to pan the view horizontally or vertically.
By mastering these basic navigation techniques, you can quickly and intuitively navigate around your 3D model and explore it from any angle.
3. Advanced Orbit Options:
In addition to basic navigation, AutoCAD’s 3D Orbit command offers several advanced options for fine-tuning your view of the model. These include:
- Pressing the Shift key twice to enter “Free Orbit” mode, which allows you to orbit the view freely without constraint.
- Holding down the Ctrl key while dragging to orbit the view around the model’s center point.
- Using the ViewCube navigation bar to quickly switch between standard views or align the view with specific faces or edges of the model.
By mastering these advanced orbit options, you can achieve greater precision and control over your 3D model and tailor the view to your specific needs.
4. Utilizing View Commands:
In addition to the 3D Orbit command, AutoCAD offers a variety of View commands that allow users to switch between different viewing modes and perspectives. These include:
- VIEW: Allows users to switch between standard views such as Top, Bottom, Front, Back, Left, and Right.
- VPOINT: Allows users to set the viewing direction and angle manually by specifying a target point and a viewing angle.
By utilizing these View commands in conjunction with the 3D Orbit command, users can quickly switch between different viewing modes and perspectives to better visualize and analyze their 3D models.
5. Conclusion:
In conclusion, mastering AutoCAD’s 3D Orbit and View commands is essential for navigating and manipulating 3D models with ease and precision. By understanding the basic navigation techniques, exploring the advanced orbit options, and utilizing the various View commands, users can achieve greater control and flexibility over their 3D models and enhance their overall 3D modeling experience. So next time you’re working with a 3D model in AutoCAD, remember to harness the power of the 3D Orbit and View commands to streamline your workflow and achieve optimal results.







